How can we know whether a document is real or fake? In today’s highly technological world, we must beware of fake or manipulated credentials or certifications, and implement standard verification practices. The rise of document falsification and diploma fraud, along with the democratization of blockchain, has led numerous companies and institutions to rethink their certification and validation methods for sensitive documents. Thanks to a decentralized and 100% traceable technology, blockchain authentication allows increased confidentiality, improved security and more transparency in business processes.
But what is blockchain exactly, and what are its benefits over traditional methods of document certification? BCdiploma takes a close look to learn more about the fundamentals of blockchain, its origins, its use in document certification and its potential applications in business.
The origins of blockchain: a decentralized and secure database
The blockchain is a shared database that allows information to be stored and transmitted in a secure manner. This online database is forgery-proof and its content verifiable.
Blockchain users are all connected through a network and have simultaneous access to a register containing the encrypted database. Every change in the register is visible to all users. Hence why it is called a distributed ledger.
Blockchain is a decentralized technology, which means it doesn’t rely on a central controlling body. Users themselves control its operation, without any other intermediary.
The history of blockchain tech
While it is currently expanding to many areas and industries, it originally came into existence along a brand-new form of currency, the famous bitcoin cryptocurrency.
In 1991, researchers Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta first mentioned the concept of a blockchain system to prevent the falsification of time-stamped documents.
Developed in the course of the 2008 financial crisis, the blockchain came to the forefront in 2009 thanks to the efforts of developers working under the pseudonym “Satoshi Nakamoto”. They were the inventors of bitcoin. Bitcoin was the world’s first cryptocurrency and sparked the blockchain revolution: due to the blockchain’s certification power, it is now possible to issue virtual currencies that are 100% certified and forgery-proof − qualifiers that were previously reserved for currencies minted by states.

In 2014, blockchain 2.0 technology was born: no longer limited to bitcoin and other virtual currencies, blockchain is expanding to much broader applications in business and education. Indeed, this technology’s immense potential has spilled over beyond the finance sector, and is frequently used in cases that require secure storing of information while guaranteeing forgery-proof traceability.
The unlimited potential of blockchain technology and promising business applications is further highlighted by the constant innovation in this field as well as the numerous projects currently under development, particularly those relating to Ethereum and the hyperledger. December 1st, 2020 saw the launch of Ethereum 2.0, the first phase of a major protocol update for Ethereum, bitcoin’s main competitor. This update will take place over the course of three phases, and introduce a small revolution in the world of cryptocurrencies: based on a proof of stake, Ethereum 2.0 blockchain technology will allow for energy savings estimated between 90 and 99%. Furthermore, IBM is developing the hyperledger, its own flexible blockchain framework. The hyperledger is an open-source modular framework designed to help developer communities build enterprise platforms and applications around blockchain technology.
What are the main advantages of blockchain technology?
Blockchain offers many benefits:
- Independence: blockchain users don’t depend on a third party, a control body or an intermediary such as banks;
- Security: the system depends on a set of users who validate the slightest change and self-manage. Moreover, it is impossible to falsify any element of the blockchain, meaning the data it contains is certified;
- Reliability: every element of the blockchain is verifiable. All users have complete visibility over the history of changes and exchanges between members;
- Efficiency: blockchain is a cost-effective technology since there is no need to pay an intermediary. It also offers significant timesavings as businesses can validate their data in just a few seconds.
How does blockchain works?
What are blocks and their “hash”?
Each blockchain is made up of a series of blocks, each containing:
- Stored information, such as transaction details contained in the block ;
- A hash: a unique sequence of numbers and letters that identify a block and everything it contains, like a fingerprint. The hash is generated when the block is created, and modified with each change made to its content;
- The previous block’s hash.
Each block is linked to the previous block through its hash. All blocks form an ultra-secure chain in which changes can be monitored by all users. If a hash changes in a block, all subsequent blocks will be impacted, invalidated and an error will automatically be detected by the program.
What is a “Proof of work”?
A new block is created whenever a user wants to enter new information into the blockchain, for instance a new transaction.
It is then up to members of the blockchain network themselves to validate and verify the authenticity of the new information inserted in the block using the proof of work. This system is made possible by some cryptographic techniques.
Once the new information has been authenticated, the new block will become visible to all users. From then on, it can no longer be modified, which is key to the security of the blockchain system as a whole.
This proof of work process slows down the creation of new blocks and prevents hackers from tampering with the blockchain by modifying a block, its hash, or by recalculating the hash of subsequent blocks.
What is the purpose of a “Proof of stake”?
The proof of stake (also called “proof of participation”) is an alternative or complement to the proof of work. It serves as an additional mode of validation to demonstrate the integrity of blocks. Proof of stake requires a user to prove possession of blocks or ownership of cryptocurrency to validate new blocks in the chain themselves.
What role do network nodes play in blockchain technology?

Blockchain works as an open network. Each user holds a copy of the ledger. When a new block is added to the chain, it is sent to the “network nodes”, a network of computers around the world. Then it is submitted for validation by each node following analysis, and added to all copies of the database.
This network of nodes helps harmonize the validity and authenticity of the blockchain certification. The majority version is the one that is considered valid.
The combination of these three mechanisms − the hash, the proof of work and the network of nodes − makes the blockchain a secure and forgery-proof technology with high probative value.
What are some concrete applications of blockchain for certification?
Blockchain certification has applications in many fields: banking, finance, insurance, health, energy, education, enterprise communication, etc.
Let’s learn more about blockchain technology’s applications in the finance and education sectors.
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies for finance
Historically, blockchain was created to support the development of cryptocurrencies and transform the world of finance, most notably with bitcoin. Cryptocurrencies are virtual currencies whose transactions are independent of any bank management.
Much more than speculative assets with ultra-volatile prices, cryptocurrencies are a genuine innovation that is revolutionizing payment systems by placing more control into the hands of users and leveraging the full power of blockchain technology.
What are the advantages of cryptocurrencies in finance?
- Decentralized currency;
- Security against fraud or theft;
- Immediate settlement;
- Very low transaction fees;
- Assurance of privacy;
- Universality (if cryptocurrencies do indeed go global).
Blockchain-based professional certifications and diplomas in training and education
Too often, professional certifications are only available in paper format, with little probative value, making them an easy target for forgery.
Forgery software is readily available and makes manipulation easy. For instance, forged diplomas or training course certificates can be bought online with just a few clicks. Of course, this creates uncertainty for employers and casts doubt on an applicant’s credibility and skills.
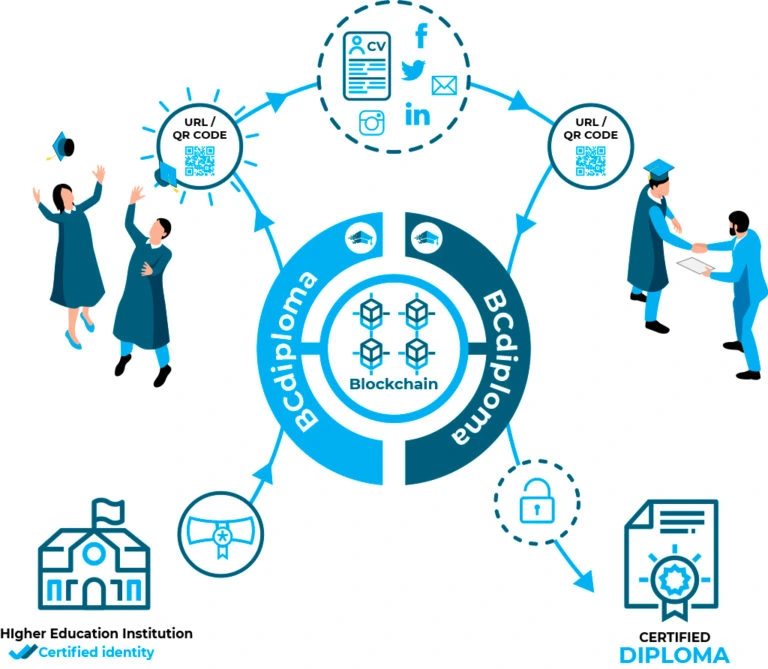
In this sense, blockchain is revolutionizing the certification system for education programs and training courses, as it allows organizations to issue digital certificates in a secure manner.
Thanks to blockchain, students receive a certified digital diploma in which all their educational information is stored, such as their validated courses. They can share this certified digital diploma on their CV, online on their social media profiles, and even send it directly to recruiters. Securing students’ diplomas on blockchain is the best way to ensure their education data is immutable and instantly verifiable.
Certificates and attestations based on blockchain are forgery-proof, meaning they help fight against increasingly widespread diploma and CV fraud. They are a wager of confidence for students’ whole professional career and give value to their acquired courses, skills, learning and other specializations.
Just like in many other sectors, blockchain is starting to show its full potential in education, as it benefits all stakeholders:
- The university protects its reputation and fights diploma fraud in a straightforward and effective manner. By implementing highly secure blockchain technology in their certified diploma issuance process, universities can of course help streamline the verification process.
- The employer reduces their hiring risk, as only a professional with certified qualifications and credentials will be employed. With blockchain authentication, businesses will witness strong efficiency improvement in their verification process, which will allow them to give quicker responses to applicants.
- The student increases their credibility and can easily share their verifiable diploma or training course certificate with future employers and on social media. They will keep these digital certifications throughout their professional career.
This innovation in the education sector has led to major initiatives in blockchain solutions for certified diplomas. Such projects aim to apply blockchain technology to certify diplomas, training courses and programs.
Ontario’s universities and colleges are pioneers in the implementation of these innovative solutions. They have chosen BCdiploma for the development of their professional micro-certification project, which will involve the creation of a 100% blockchain certified Open Badge.
In France, emlyon business school is the first business school to implement blockchain certification on a large scale. They will offer certified digital credentials diploma service to their 18,000 alumni, turning their institution into a leader in digital innovation in higher education.
BCdiploma’s 100% blockchain certifications
BCdiploma specializes in 100% blockchain certified diplomas, attestations, badges and micro-certifications.
BCdiploma’s blockchain technology ensures that training organizations and companies have direct, decentralized access to certified micro credentials.
Each digital certificate based on blockchain technology is 100% secure, verifiable, forgery-proof and designed for unlimited sharing online across all media.
BCdiploma’s micro-certifications and blockchain certified badges will enable the certification of graduates’ acquired skills in the framework of training organizations implementing new skills blocks.
BCdiploma provides companies with an integrated and fluid digital platform to streamline the management of online attestations.
Discover 3 reasons to opt for blockchain-based degree with BCdiploma.
FAQ
How does blockchain certification work?
The certified document’s unique fingerprint is secured on a worldwide network of blockchain nodes. This certificate’s data is 100% secure and tamper-proof, and its integrity and origin can be instantly verified. Thanks to turnkey online solutions, no prior developer or expert blockchain knowledge is needed to certify a document.
What are the main benefits of blockchain?
Blockchain increases trust and transparency by improving the traceability of data shared across a business network. It improves security by creating an unalterable record of certified transactions with end-to-end encryption, which prevents fraud and unauthorized activity. Finally, it’s one of the best ways to deliver cost savings at scale as it helps process transactions more efficiently.
How can blockchain solve the scourge of fake diplomas?
Blockchain allows universities to issue digital, certified and tamper-proof diploma to their graduates. This technology is the best solution to certify a course, learning or training program, as it provides optimal security.
Learn more:
https://www.ibm.com/fr-fr/topics/what-is-blockchain
