More reliable and efficient, the blockchain builds trust in the Digital Credential ecosystem.
The term “Credentials” encompasses the notions of diplomas, qualifications, references, authorizations or professional titles. They are part of our daily lives: driver’s licence, university diploma, transcript, passport… Most of them are in physical form: plastic cards, identity papers, paper diplomas for example. The blockchain opens up new possibilities and accelerates the potential for dematerializing these documents. Let’s not miss the point: these documents are often fundamental to our governmental, social and professional organizations.
What are Digital Credentials?
The Digital Credentials are digital certificates issued by an institution. Diplomas, skills or transcripts for the educational world are digital credentials examples. The blockchain, a decentralized, long-lasting and forgery-proof database, makes it possible to secure and store these documents. Students, graduates and citizens thus have a lifetime supply of authentic certificates that can be freely used and instantly verified without any procedure.
Why are they more reliable?
Storage on the blockchain makes changing documents and data impossible: this is called blockchain immutability. These credentials are therefore impossible to falsify.
Why are they more efficient?
Students, graduates and citizens have lifetime certificates that can be accessed online with only one click and shared on all media and professional networks. Immediate added value for the certificate holder. No more inopportune verification requests, updating of certificates or duplicates: a long-term benefit for the Institution issuing the certificates.

Why do they build trust?
The authenticity of the documents is guaranteed, with no further verification to be carried out: this is known as Verifiable Credentials. W3C’s mission is to standardize these Verifiable Credentials to ensure a globally recognized exchange format for academic credentials. It issued its first recommendation in November 2019.
BCdiploma is a natively compatible solution with this micro credential example standard: its technology is based on a patented blockchain framework. It allows direct access to a set of significant data secured on chain, without constraining it to a format or template. The protocol, which is non-prescriptive by design, is therefore designed to support the development of sectoral standards.
What is the main principle of a Digital Credential?
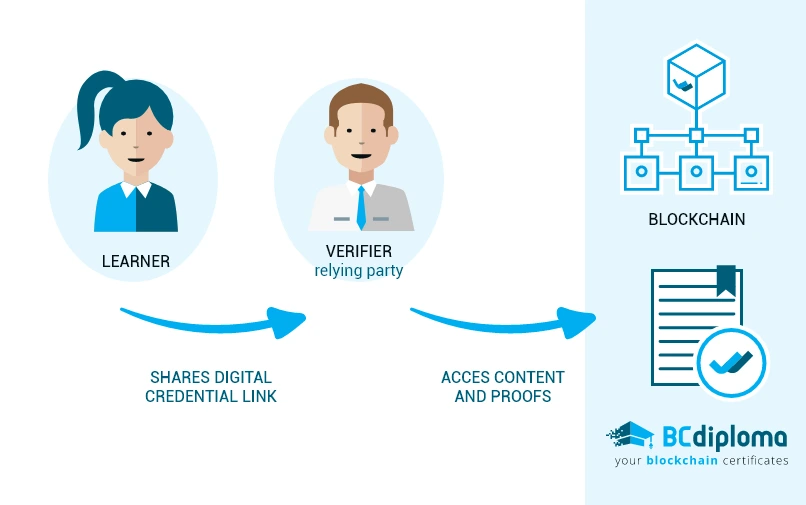
An issuer publishes a certificate and provides its learner (to quote the semantics of the Digital Credentials Consortium) with the right to use it. The third party viewing the certificate (verifier or relying party) shall have direct access, without asking the issuer, to a verifiable set of proofs of the identity of the issuer, the learner and the validity of the certificate.
In most ecosystems, such as the one specified by the Digital Credentials Consortium, the blockchain is used to secure indirect proof, i.e. a timestamp (a “unique digital signature”) to determine whether a certificate is identical to its original version.
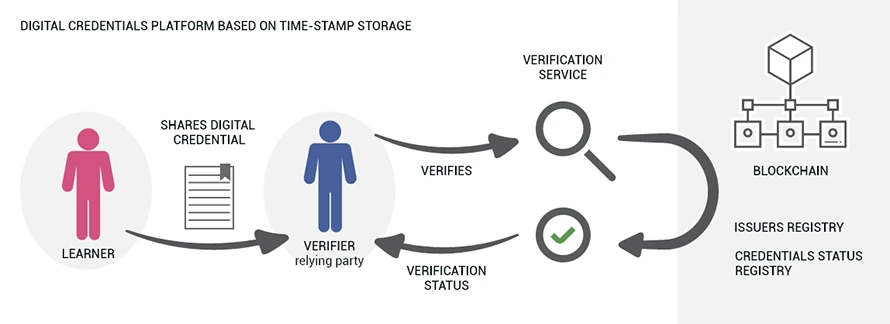
On the other hand, BCdiploma allows to directly secure all the relevant data: you can directly access the content of the certificate and not only its validity information.
Groundbreaking, but is it long-lasting?
The use of public blockchains makes it possible to guarantee unlimited storage of data over time, and this is one of the reasons why it has been adopted in the field of “digital credentials”. Discover more about Digital Credentials: legal proof and data privacy.
The BCdiploma ecosystem is designed to be able to work… without BCdiploma.
Data storage and accessibility of certificates are guaranteed independently of a service contract or performance contract: welcome to the blockchain era!
